Install Instructions
Prerequisites
Before starting the installation, ensure you have the following:
Required
- A server or virtual machine (CPU node) with internet access to host Transformer Lab.
- AWS account and credentials (for S3 storage) with permissions to create and manage S3 buckets.
- SSH access to the server.
- Bash shell.
- curl command.
- Administrative (sudo) privileges.
Feature-Specific
- SkyPilot server running and accessible from the CPU node (e.g., via IP).
- SLURM cluster access from the CPU node (e.g., via SSH).
Step 1 - Set up a Cloud Provider
Transformer Lab executes tasks by sending them to a GPU orchestrator like SLURM or SkyPilot. So your first step in setting up Transformer Lab is making sure you have a properly configured SLURM or SkyPilot instance.
The following documents offer common install instructions that you can use if you are starting from scratch
Choosing Between SLURM and SkyPilot -->
Instructions for setting up SLURM from scratch -->
Instructions for setting up SkyPilot from scratch -->
Step 2 - Install Transformer Lab
Transformer Lab needs a CPU node to run.
SSH into that node and run:
curl https://lab.cloud/install.sh | bash
You need to also install packages necessary for running compute providers like Skypilot or SLURM:
cd ~/.transformerlab/src
./install.sh multiuser_setup
Step 3 - Run Transformer Lab and Log in
Run Transformer Lab by running
cd ~/.transformerlab/src
./run.sh
Now you can visit http://localhost:8338 (or the address of the server you have put this code on) and log in to Transformer Lab.
The first time you log in, you can use the default user:
Login: admin@example.com
Password: admin123
Please change the password as a first step.
Step 4 - Configure Team Edition
Now create a file in ~/.transformerlab called .env
And copy and paste the following information (update localhost to your server address):
TL_API_URL="http://localhost:8338/" # API runs by default on port 8338
MULTIUSER="true" # Set to "true" to enable multi-user features
# In a default setup, the frontend URL will be the same as the API URL set above.
FRONTEND_URL="http://localhost:8338"
# Setting this to true uses the transformerlab-s3 profile in your AWS credentials to create and use a S3 bucket as your remote workspace
TFL_API_STORAGE_URI=true
Setting up AWS Credentials for S3 Storage
To use S3 as remote storage, you need to configure AWS credentials for the transformerlab-s3 profile. You can do this in two ways:
Using AWS CLI (Recommended)
If you have the AWS CLI installed, run:
aws configure --profile transformerlab-s3
Enter your AWS Access Key ID, Secret Access Key, default region, and output format when prompted.
Manual Configuration
Create or edit the AWS credentials file at ~/.aws/credentials and add:
[transformerlab-s3]
aws_access_key_id = YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID
aws_secret_access_key = YOUR_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
Ensure the profile has the necessary permissions to create and manage S3 buckets.
Step 5 - Configuring a Compute Service
Go to Team Settings by clicking your user name in the sidebar.
In Team Settings, open Compute Providers and click "Add Compute Provider." Name the provider, choose a type (either "skypilot" or "slurm"), and then add the configuration.
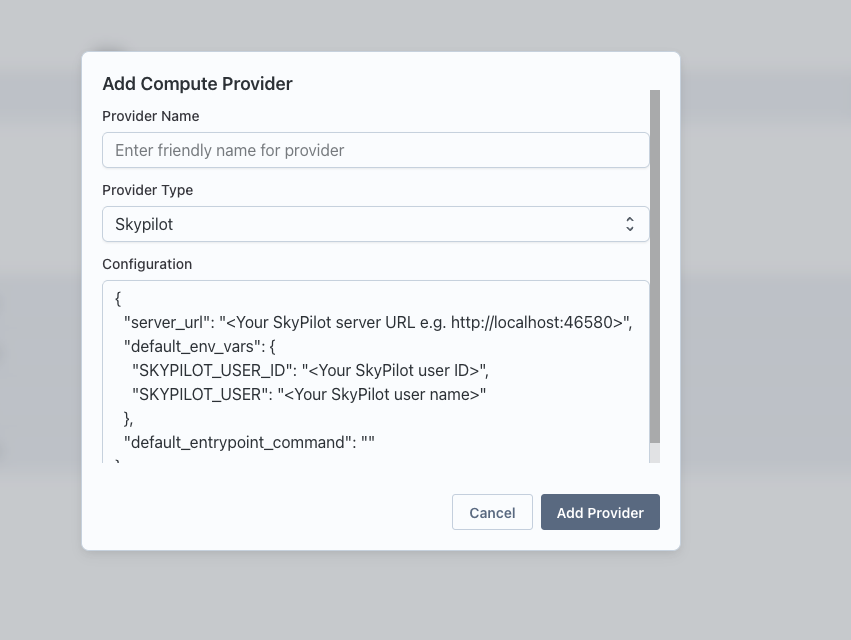
SkyPilot example config
{
// Replace with the IP/host of your SkyPilot server reachable by the API server
"server_url": "http://localhost:46580",
"default_env_vars": {
// Obtain from the SkyPilot server at http://<skypilot-host>:46580/users
"SKYPILOT_USER_ID": "<skypilot user id>",
"SKYPILOT_USER": "<skypilot username>"
},
"default_entrypoint_command": ""
}
- Replace
localhostwith the IP/hostname where your SkyPilot server is running and reachable from the API machine. - Retrieve
SKYPILOT_USER_IDandSKYPILOT_USERfrom the SkyPilot server athttp://<skypilot-host>:46580/users.
SLURM example config
{
"ssh_host": "<SLURM_LOGIN_NODE_IP>",
// Many clusters use the "slurm" user; use the appropriate user for your setup
"ssh_user": "slurm",
// Path to your SSH private key
"ssh_key_path": "~/.ssh/id_rsa",
"ssh_port": 22
}
- Ensure the API node can SSH to the SLURM login node with the provided user and key.
- Adjust
ssh_user,ssh_key_path, andssh_portto match your cluster configuration.
Congrats, you are up and running. You can now run a Task -->