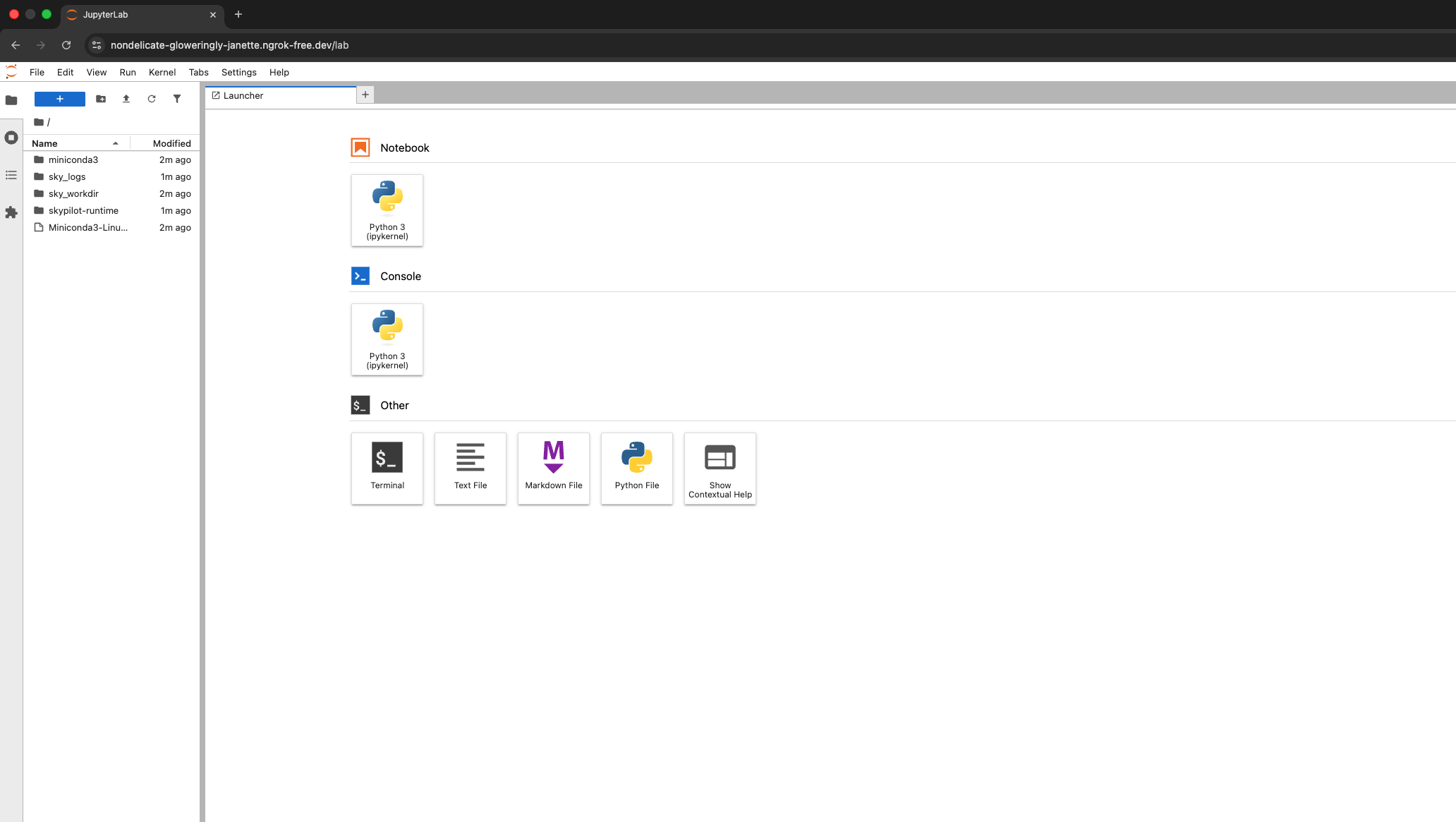
Running an Interactive Service
What is an Interactive Service?
Transformer Lab supports two distinct types of workloads, designed to map to the different ways researchers work: Tasks and Interactive Services.
Tasks vs. Interactive Services
- Tasks (Batch Workloads): These are jobs that are queued and scheduled to run automatically when the necessary resources become available. They execute a set of instructions and terminate upon completion. A commoon usecase would be for training a model.
- Interactive Services (On-Demand): These workloads function like a reservation. When you launch an Interactive Service, a specific computer or set of resources is held exclusively for you. It remains active and available until you explicitly release it.
Common Use Cases for Interactive Services
Interactive Services are best suited for workflows that require persistent access or real-time interaction.
1. Model Inference
Interactive services are ideal for hosting models that need to stay online to serve requests.
- Examples: Running inference servers like Ollama or vLLM to host a model in the cloud and query it via API.
2. Exploratory Research & Development
In the early stages of research, you often need an environment to experiment, debug, and iterate quickly without waiting for a queue.
- Tools: Gain direct access to the compute resources via VSCode, Jupyter Notebooks, or SSH.
- Workflow: Use an Interactive Service to prototype your code. Once your script is finalized and stable, you can convert it into a Task to run large-scale training jobs efficiently.
Prerequisites
Before running an interactive service, ensure you have a Compute Provider set up and active.
-
Navigate to Team Settings and set up a Compute Provider.
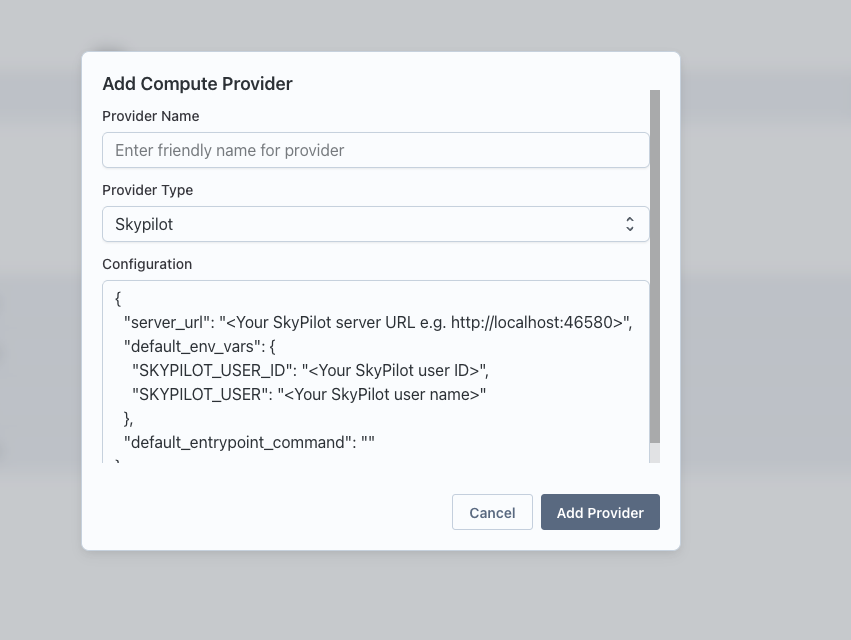
-
Make sure the provider is active by clicking on the health button.
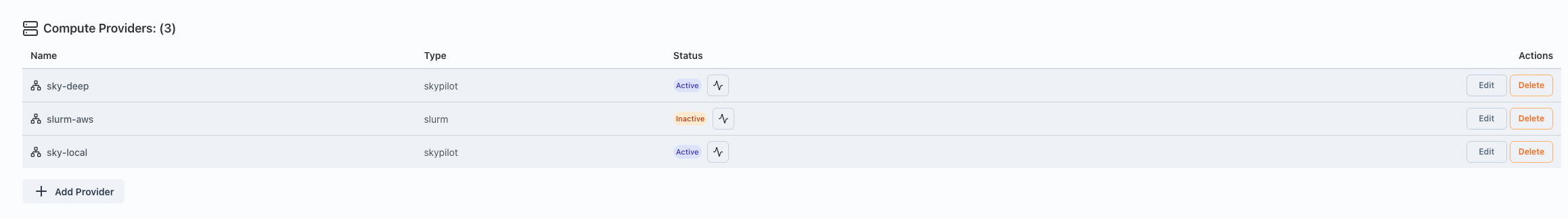
Steps to Run an Interactive Service
-
Go to the Interact page in Transformer Lab.
-
Click on the "New" button to create a new interactive service.
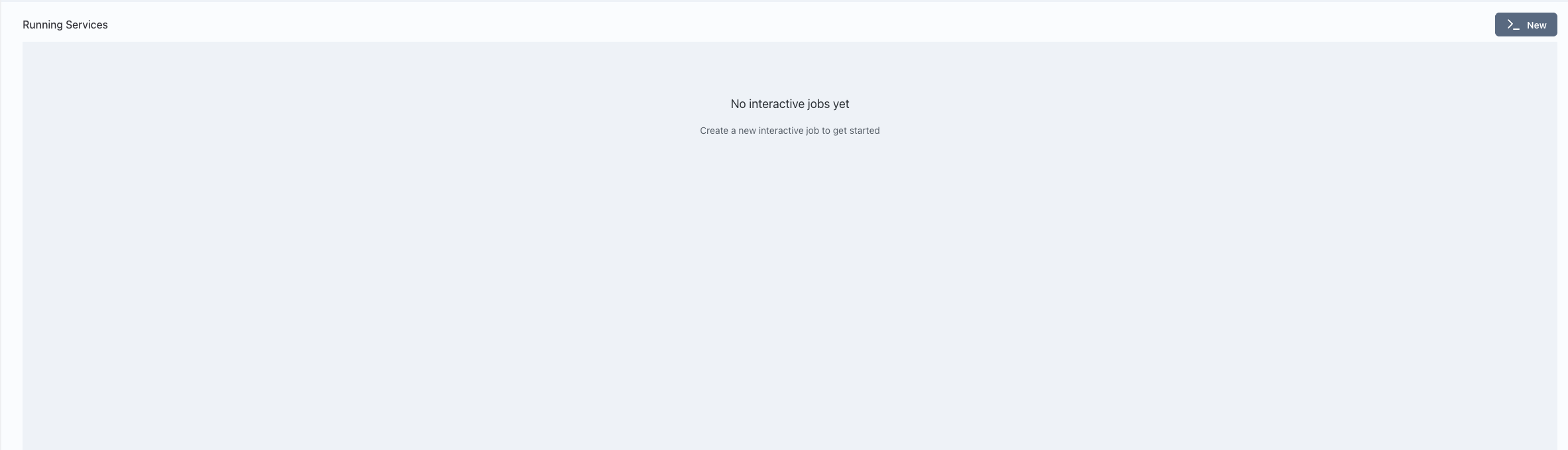
-
Select the type of interactive service you want to launch: VSCode, Jupyter Notebook, SSH, vLLM Server, or Ollama Server.
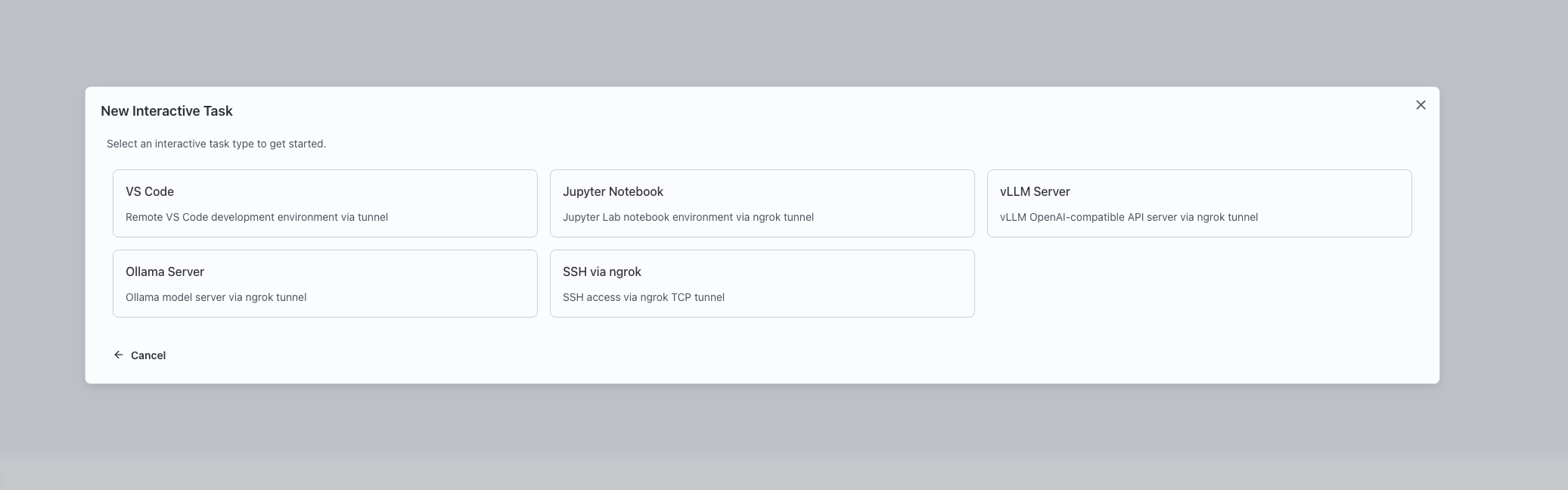
-
Configure the service:
- Enter a name for the service.
- Select the Compute Provider to use.
- Specify the resources: CPU, memory, and GPUs.
- For certain services, provide additional inputs such as model_name for vLLM Server or ngrok auth token for services that launch a tunnel.
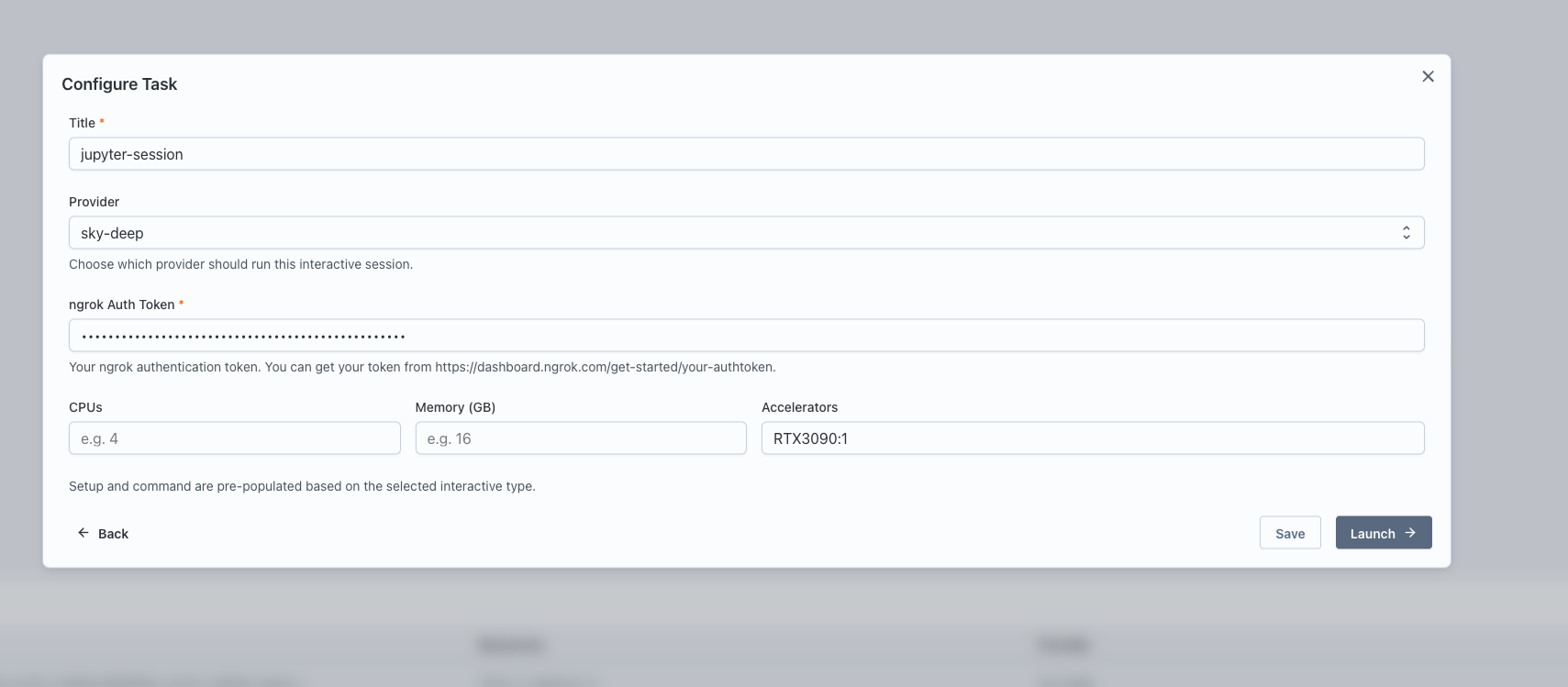
-
Click "Launch" to start the service.
-
Once launched, a card will appear for the service. Click the "Interactive Setup" button on the card.
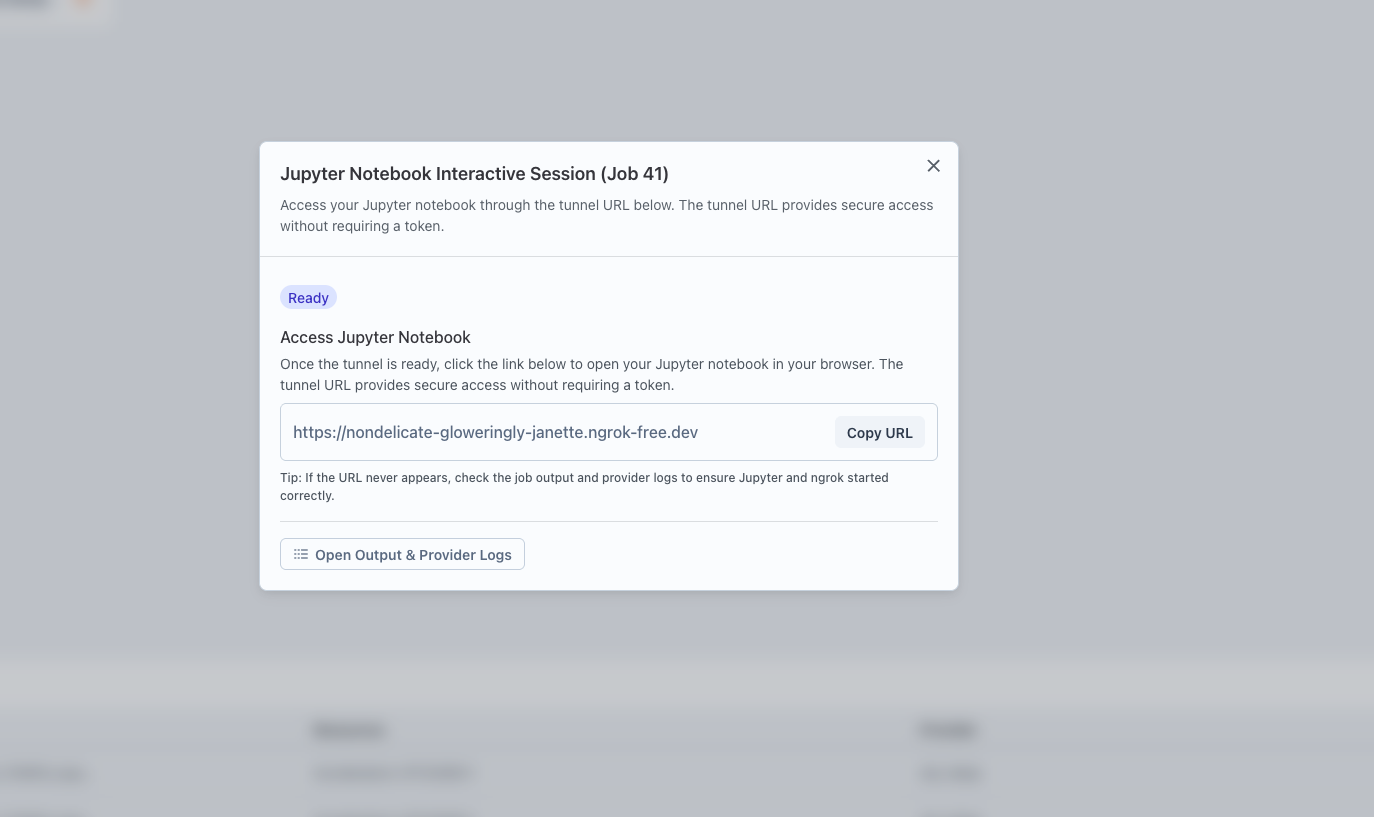
-
Follow the provided URL or steps to access the service.